What are OERs?
Open Educational Resources (OER) are free resources available to teachers and students alike. Many have the ability to be used, adapted, shared, and reused. They can include any type of educational resource and are defined as:
- Openly-licensed
- Freely available
- Modifiable
OERs break down the barriers of affordability and accessibility for students and give instructors the ability to adapt their content to the needs of their students each year. There are a variety of resources such as textbooks, videos, supplemental materials, and software available for instructors to use.
“In the context of education, it comes down to sharing. At the end of the day, an educator is sharing knowledge and passion – that’s what you are doing, and ought to be doing.”
-David Wiley
The information in this section was adapted from The OER Starter Kit by Abbey K. Elderper per the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Why use OER?
OERs are readily available for instructors and students alike. It has been shown that OERs increase student learning, are more affordable for students, and can be made to be easily accessible for all. The inclusion of OER in a course can provide students access to a variety of types of materials in order to learn material in different ways. It is also helps instructors the ability to adapt materials to the specific needs of their students. Additionally, some OERs are updated regularly by other authors, giving instructors a choice to what materials they use from year to year in the classroom and/or they can tailor them to be up to date.
What are the Benefits?
There are a multitude of benefits for students and instructors when adapting OER. Open education resources perform as well or better than their traditional counterparts. They are widely available and easy to use for instructors and students.
Affordability
Perhaps the most common reason many instructors begin looking for OERs for classes is affordability for students. Traditional textbook costs have increased over 80% in the past decade. Students have had to bear the burden of these increasing textbook costs. Many students will either buy textbooks later into the semester, waiting to see if the instructor will use them, or forgo buying them altogether. Studies have shown students were more likely to get the textbook for a class if they were free or affordable (~$40). This in turn leads to students doing better in that class with a free/affordable textbook versus classes that require an expensive textbook they may not be able to afford.
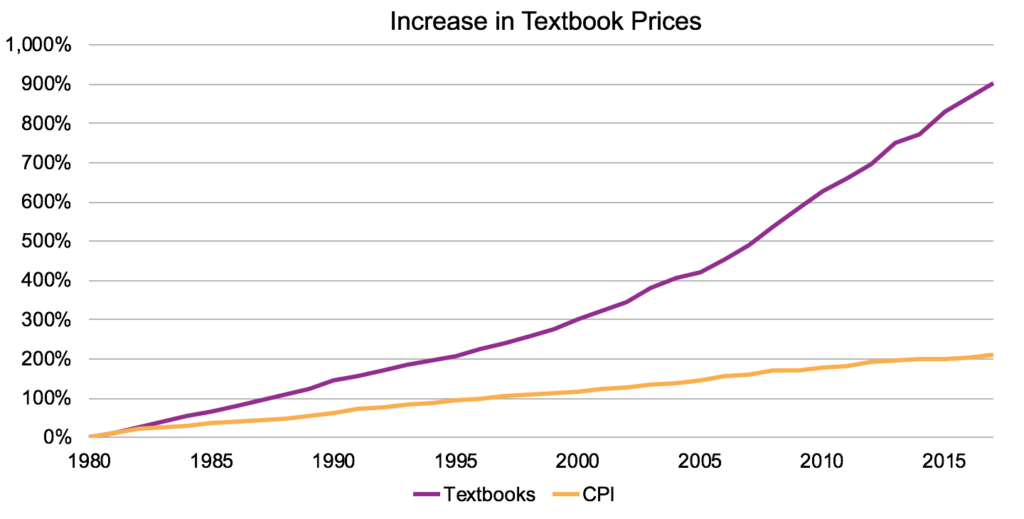
This chart shows the price of college textbooks outpacing all other consumer goods in the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
“Increase in Textbook Prices” by David Ernst, the Open Textbook Network, is licensed CC BY 4.0. Data source: Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Additional Benefits for Students
- Better performance and lower fail/drop rates.
- Fewer barriers to learning for a wider range of students.
- Multiple ways to access the material.
- Can support and enhance self-learning/peer-to-peer learning depending upon chosen materials.
- Can expose students to a wider range of digital learning opportunities or modalities.
- Can allow students to see and apply knowledge in a wider or more current context.
Benefits for Instructors
Instructors have access to large, online repositories OER content to use in their classes; however, this is not the only benefit to using open educational resources in your classes.
- Adapting and revising existing resources to fit your course specific needs.
- Accessing education resources that have been peer-reviewed by others in that field.
- Creating a new open education resource with a team of your peers or colleagues.
- Providing all students equal access and the opportunity to explore course content without financial barriers.
- Supplementing existing curriculum resources and customization.
- Updating and revising materials to meet current needs.
- Adapting materials to your teaching style.
- Customizing quizzes, homework, and other supplementary materials.